Sciatica
Sciatica the 6 main causes
There are several different disorders of the lumbar spine (lower back) that can cause sciatica. It is often described as moderate to severe pain in the left or right leg. Sciatica is caused by the compression of one or more of the five groups of nerve roots in the lower part of the back. Sometimes doctors call sciatica a radioculopathy. Radioculopathy is a medical term used to describe pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the arms and legs caused by a nerve root problem. If the problem is in the neck, it is a cervical radioculopathy. However, because sciatica affects the lower back, it is called lumbar radioculopathy.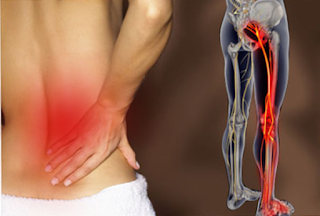
Pathways leading to sciatic nerve pain Five pairs of nerve roots that create the sciatic nerve are combined in the lumbar spine. The sciatic nerve starts from the posterior part of the pelvis (sacrum) and runs down the back, under the buttock, and down, crossing the hip area towards each leg. The nerve roots are not"solitary" structures, but are part of the complete nervous system, capable of transmitting pain and sensations to other parts of the body. Radioculopathy occurs when the compression of a nerve root occurs due to rupture of a disc or bone spurs in the lumbar spine before it attaches to the sciatic nerve.
Sciatic nerve compression
 Different types of spinal disorders can cause compression of the spinal nerve and sciatica or lumbar radioculopathy. The six most common are: (1) bulging or herniated disk, (2) lumbar spinal stenosis, (3) spondylolisthesis, (4) trauma, (5) piriformis syndrome and (6) vertebral tumors. Each condition is briefly explained below.
Different types of spinal disorders can cause compression of the spinal nerve and sciatica or lumbar radioculopathy. The six most common are: (1) bulging or herniated disk, (2) lumbar spinal stenosis, (3) spondylolisthesis, (4) trauma, (5) piriformis syndrome and (6) vertebral tumors. Each condition is briefly explained below.(1) Lumbar bulge or herniated disk
The bulging disc is also known as disc disc disorder. This means that the gelatinous center (nucleus pulposus) remains "contained" within the outer wall in the form of a tire (fibrous annulus) of the disc. A disk hernia occurs when the nucleus breaks through the anulus and is called a "non-contained" disc disorder. Whether the disc is bulging or herniated, the material inside it can press against an adjacent nerve root and compress the delicate nerve tissue causing sciatica. The consequences of a herniated disc are worse. The herniated nucleus not only directly compresses the nerve root against the inside of the bone vertebral canal, but also, the same disc material contains an acidic chemical irritant (hyaluronic acid) that causes inflammation of the nerve. In both cases, compression and irritation of the nerve cause inflammation and pain, which often leads to numbness of the extremities, tingling and muscle weakness.(2) Lumbar spinal stenosis
Spinal stenosis is a nerve compression disorder that usually affects older people. As a result, leg pain similar to sciatica can occur. The pain is usually positional: it is often caused by activities such as standing or walking and is relieved by taking a seat. The spinal nerve roots branch out of the spinal cord through passages called neural foramines composed of bone and ligaments. There is a foramen between each group of vertebral bodies, located on the left and on the right. The nerve roots pass through these openings and extend outward beyond the spinal column to innervate other parts of the body. When these passages narrow or clog causing nerve compression, the term foraminal stenosis is used.(3) Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is a disorder that most often affects the lumbar spine. It is characterized by the sliding of a vertebra forward over the adjacent vertebra. When a vertebra slips and moves, compression of the spinal nerve root occurs and often causes sciatic pain in the leg. Spondylolisthesis is classified as developing (found at birth and developing during childhood) or acquired by spinal degeneration, trauma or physical stress (ie, weight lifting).4) Trauma
Sciatica can be the result of a direct compression of the nerve caused by forces external to the lumbar or sacral spinal nerve roots. Examples include automobile accidents, falls, football accidents and other sports. The impact can damage the nerves and occasionally fractured bone fragments can compress the nerves.(5) Piriformis syndrome
The name of this syndrome is due to the piriformis muscle and the pain it causes when it irritates the sciatic nerve. The piriformis muscle is located in the lowest part of the spine, connects with the femur and helps in the rotation of the hip. The sciatic nerve is located below the piriformis muscle. This syndrome develops when there are muscle spasms in the piriformis muscle that compress the sciatic nerve. Your diagnosis and treatment can be difficult due to the lack of results through radiographs or MRI.(6) Vertebral tumors
Vertebral tumors are abnormal growths that can be benign or cancerous (malignant). Fortunately, vertebral tumors are not frequent. However, when a vertebral tumor develops in the lumbar region, there is a risk that sciatica will develop due to compression of the nerve.If you think you suffer from sciatica, contact a spine specialist in your community. The first step towards pain relief is an adequate diagnosis!






No comments